Welcome to Greenify! Subscribe now and thank us later for not missing the most insightful information on the booming #GreenTransition!
Please help us improve by leaving a comment or feedback, and if you like what you are learning… share it with your network 😁!
📌 Fact of the week
Global government spending to support clean energy has increased by over $500B since Russia’s invasion of Ukraine, according to the IEA.
Hottest news of the week…
Regulation 🗃 – The World Bank’s efforts
What happened: The World Bank aims to raise additional funds in order to better address climate change and other issues. They plan to do so through 1) increase in capital and 2) the establishment of new financing tools from member countries. In this way, the World Bank will be able to act as a guarantor for more private investments and hence mobilize more private capital in a race to slow down global warming. 💪
Zoom out: The World Bank’s roadmap is designed to commit adequate resources for the challenges the world is facing today. In fact, the existing budget of the World Bank’s “crisis division” were designed to withstand one mid-size crisis per decade, and not multiple overalapping crisis, such as Covid-19, increasing global warming, and the energy crisis. If successful in raising more funds, the remaining challenge for the World Bank will be to increase climate commitments while improving development opportunities for poor countries.😬
Business 💰 – Eni’s quest to net-zero continues
What happened: As announced in March, Italy’s energy giant Eni has set up “Eni Sustainable Mobility”, a company 100% controlled by Eni dedicated to, guess what?, sustainable mobility! The company will act along several stages of the value chain, developing bio-refining, biomethane, and offering mobility products and services in Italy and abroad. 🔋
Zoom out: Eni Sustainable Mobility follows Plenitude’s set up by Eni, another subsidiary supporting the group’s energy transition initiatives. Given the size of the energy majors and the amount of assets, capital and expertise they possess, the transition to net zero will be inevitably starting from these companies, in our view. Eni is not the first one and won’t be the last, as we expect more positive news this year. 🥇
Innovation 💡 - Grounding panels
What happened: A new 100 MW solar plant is being built in Texas. What’s innovative about it? The panels will be placed directly on the ground! This new method was developed by Erthos, a US-based company, which claims that it allows for construction of a solar farm saving 1/2 of the time, 1/3 of the land, using 70% less cables and an overall 20% cost reduction vs. traditional farms. As a result, this method would produce 5 or 6 MW per acre, compared to the 2.5 MW of a traditional farm. 🔝
Zoom out: Although some limitations exist, solar panels laid on the ground can be an alternative method for traditional solar farms, as the 20% cost reduction is huge in the utilities world. Additionally, this method could increase the resilience of solar panels to climate disasters, such as hurricanes, and therefore could find a perfect use case on the US’ east coast! 👍
Deep dives of the week…
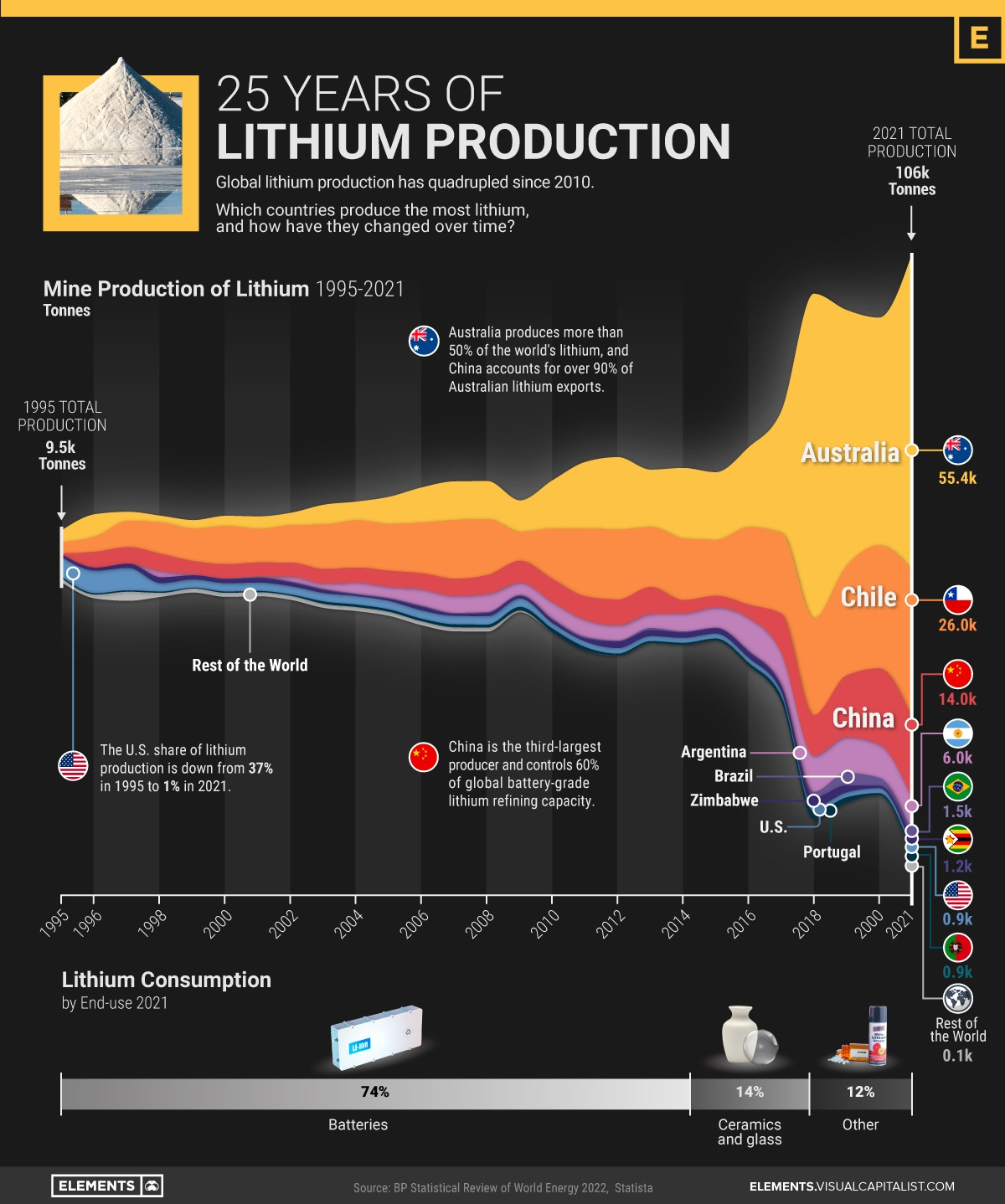
Graph of the week - Where does Lithium come from?
Lithium, often referred as the “white gold”, is a fundamental component for rechargeable batteries. We have recently been hearing about demand for lithium exceeding global supply at this moment in time, slowing down the energy transition; hence we wanted to show where this metal comes from.
The main producer is Australia with 52% of share, followed by Chile with 25%, and China with 13%, equalling 90% among the three countries. However, the country of origin does not tell the whole story, as Chinese companies have acquired c. $5.6B worth of lithium assets around Australia, Chile, and Canada! So yes, once again, we are heavily dependent on Chinese companies to pursue the energy transition 😬
Company of the week - Heat pump disruption
In Greenify #9, we had provided you with an introductory guide to heat pumps and how they are set to take over gas boilers over the next decades as the main heating systems in our planet’s transition to net-zero. In the context of a fast-growing market, this week’s company is Qvantum, which just raised €42M despite market turbulence. The funds will be used to accelerate launch of next-gen electric heat pumps as well as finalising the company’s new production site in Åstorp, with an annual capacity of 50k heat pumps.💸
Analysis of the week - Mirroring the sun ☀️
In last week’s edition we featured Make Sunsets in our newsletter, a company active in solar engineering. This week, we’ll provide you with a brief summary of another similar technology, space mirroring.
1) What are space mirrors?
Space mirrors are an example of solar radiation management, a set of practices looking to leverage solar radiation to the planet’s advantage. Space mirroring specifically comprises a set of technologies used to try and reflect sunlight back into space. 🌍
2) How does this work?
Orbiting mirror systems are sun shields positioned in space to reduce the amount of solar energy reaching the earth. These reflectors are expected to block out approximately 1.8% of solar rays from coming to earth. 🪞
3) What are main barriers?
Two significant barriers limit space mirroring’s potential: 1) this technology is very expensive, and 2) it has unknown weather effects and can lead to unintended climate changes.
Source: The Sydney Morning Herald
👋 See you next Friday, for the best sum up of this coming week!
If you enjoyed this edition, help us grow by liking this post, and share it with your network!